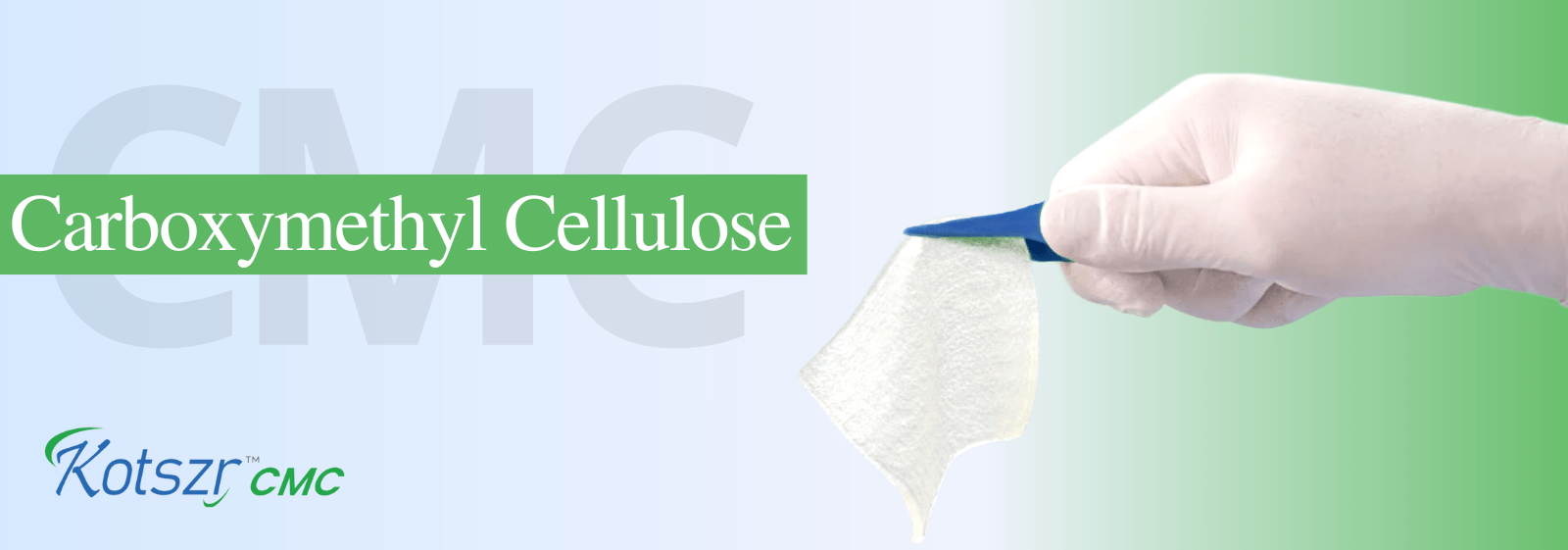
It is designed to provide High absorbency and Tensile Strength for enhanced patient comfort. Technologically advanced blend of Carboxymethyl cellulose and Non- modified cellulose fibres, to ensure accelerated wound healing.
It has been designed with a unique construction that allows for intact removal and easier dressing changes.
Key Features

Fluid Lock-In

Soft and Conformable

Can be used Under Compression

Protects peri wound area from Maceration

High Absorbency with Excellent Tensile Strength

High Vertical Absorption Limits the Spread of Fluid to Wound Edges
Mechanism of Action
Fluid Lock-In
Micro Contours
Responds
Use Cases
Indicated for use on wounds that are Infected or are at Risk of Infection.
Venous Leg Ulcer
Burns
Pressure Ulcer
Cavity Wound

Donor Site
Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Abrasion
Laceration
How to use?
Always use the Aseptic Technique
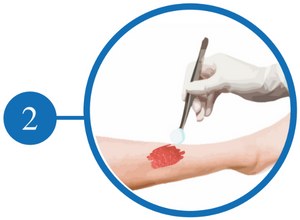
Clean and Irrigate the Wound
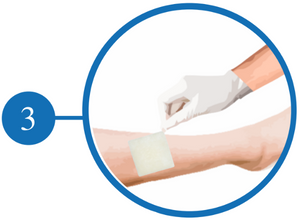
Folding make sure it fits the Wound
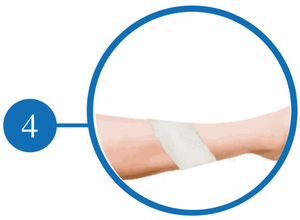
Apply a Secondary Dressing
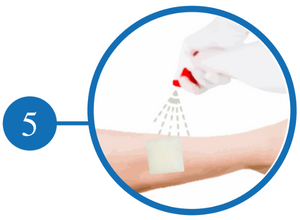
Irrigate with Saline and Gently Peel Off
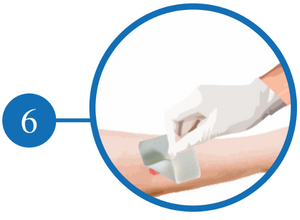
Remove the dressing Slowly and Discard It
Clinical Data
Absorbency
- This dressing has demonstrated greater absorbency compared to other commercially available brands.
- Good Exudate Management promotes positive healing progression of the Wound.

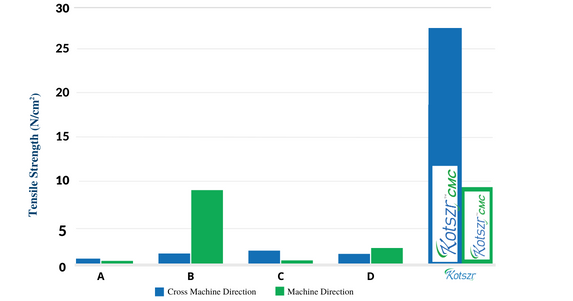
Wet Tensile Strength
• This dressing has significantly higher wet tensile strength when compared to other commercially available brands.
• It aids in easy, trauma-free removal of dressing from the wound site.
Lateral Wicking
- This dressing has the ability to immobilize absorbed fluids and prevent the lateral spread of exudate.
- Its dressing controls fluid circulation in the wound, avoiding peri-wound maceration.
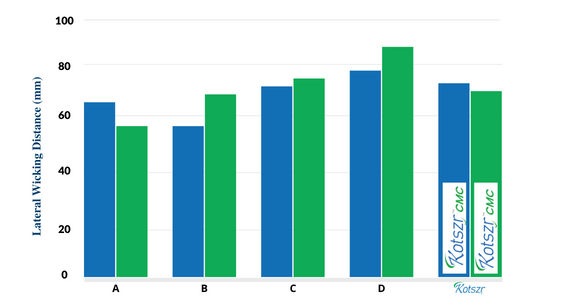
A – Aquacel is a registered trademark of ConvaTec | C – Durafiber is a registered trademark of Smith & Nephew
B – Aquacel Extra is a registered trademark of ConvaTec Inc. | D – Exufiber is a registered trademark of Mölnlycke
In-Vitro Analysis
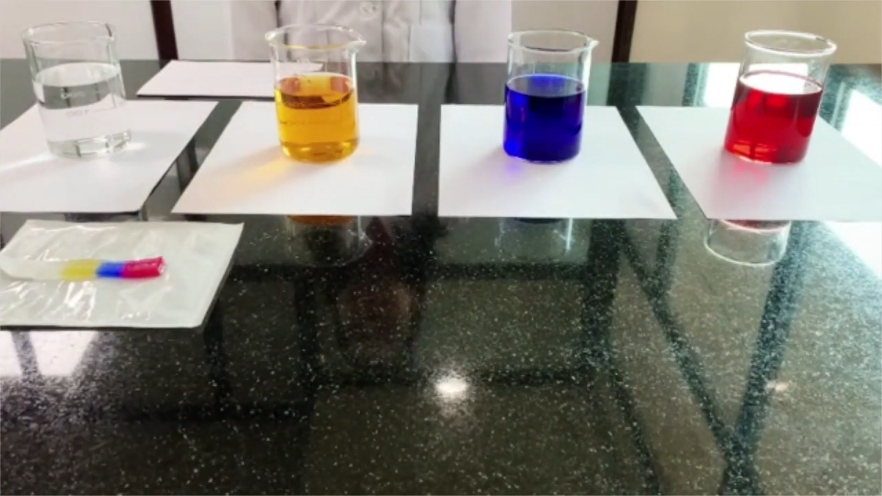
Sequestration Test
- This in-vitro experiment uses different coloured fluids to illustrate the ability of the dressing to lock in the fluid that is absorbed compared to conventional alginate dressings.
- As, Kotszr is placed in the different coloured fluids, we can see how the dressing locks in the different coloured fluids in turn with the result that there is no bleeding of the colours into one another.
- In contrast, the conventional alginate dressing fails to lock in the fluids which results in the colours bleeding freely into one another.
- The ability of a dressing to lock in fluid is important for helping to remove excess fluid and any harmful bacteria it contains away from the wound bed and may reduce the risk of cross contamination on dressing removal.


Lateral Wicking Test
• This in-vitro experiment illustrates the ability of the dressing to lock in absorbed fluid and to control the lateral spread of exudate.
• Once applied, Kotszr rapidly wicks the fluid away from the surface of the petri dish, (representative of exudate in a wound bed). The absorbed fluid does not spread to the outer edges of the dressing but is contained within the area of the simulated wound bed.
• The conventional alginate is quickly saturated and lets fluid wick freely in all directions.
• The ability of a dressing to control the lateral spread of fluid is important in helping to minimise the risk of peri-wound maceration.
